BECE 2002 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Which of the following substances is made up of only one kind of atom?
Solution: Iron is an element composed solely of iron atoms. Salt (NaCl) is a compound, steel is an alloy (mixture), and water (H₂O) is a compound—all contain multiple types of atoms.
2. Ice is able to float on water because the ice is
Solution: Ice floats due to lower density than water. For the same mass, ice occupies more volume (option D), while denser substances (B) or heavier masses per volume (C) would sink.
3. Which of the following statements about the state of matter is correct?
Solution: Gas molecules move faster than liquid molecules due to higher kinetic energy. Solids have ordered molecules (A), are incompressible (B), and liquids lack definite shape (C).
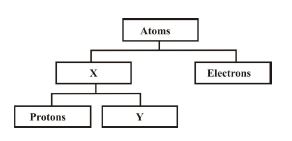
4. The above diagram illustrates the structure of an atom. The components labeled X and Y are respectively
Solution: X represents neutrons (neutral particles in the nucleus), and Y is the nucleus (central part containing protons and neutrons). Shells hold electrons, not labeled here.
5. The force which opposes the motion of one object on another object is known as
Solution: Friction resists relative motion between surfaces. Gravity pulls objects downward, tension acts in stretched materials, and weight is gravitational force.
6. When the brakes of a bicycle in motion are applied for a long time the wheels become hot. This is because of a change of energy from
Solution: Braking converts kinetic energy (motion) into heat via friction. No potential energy (stored) is involved here.
7. A man applied a force of 50 N to push a wheelbarrow through a distance of 6 m. Calculate the work done.
Solution: Work = Force × Distance = 50 N × 6 m = 300 J. Other options miscalculate the formula.
8. In which of the following situations is work said to be done?
Solution: Work requires force and displacement. Walking with a load (A) and rising from a chair (B) involve displacement. Pushing a static wall (C) and sitting (D) lack displacement.
9. The energy stored in food is
Solution: Food energy is chemical, stored in molecular bonds (e.g., carbohydrates). Electrostatic, solar, and thermal energies are unrelated.
10. A machine which has an energy loss of 10% will have an efficiency of
Solution: Efficiency = 100% - Energy loss = 100% - 10% = 90%. Losses reduce efficiency proportionally.
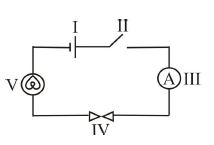
The figure below shows a simple electric circuit. Use it to answer questions 11 to 13
11. The switch is represented by
Solution: In standard circuit diagrams, a switch (component II) controls current flow by opening/closing the circuit.
12. The component labeled V is a/an
Solution: Component V (likely a bulb) is a lamp converting electrical energy to light. Batteries supply energy, meters measure.
13. The purpose of the component labeled IV is to
Solution: Component IV (likely a resistor) limits current to protect components. Switches close circuits; batteries supply energy.
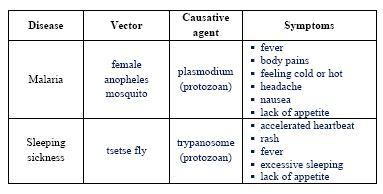
14. Which of the following diseases is spread by a mosquito?
Solution: Elephantiasis (lymphatic filariasis) is transmitted by mosquito bites. Cholera/dysentery are waterborne; blindness isn’t directly spread.
15. The intermediate host of the worm that causes Bilharzia is
Solution: Bilharzia (schistosomiasis) involves water snails as intermediate hosts for parasitic larvae. Humans are definitive hosts.
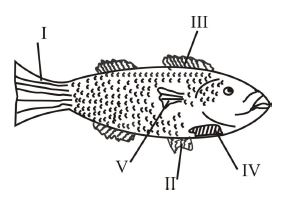
The figure below is a diagram of a fish. Use it answer questions 16 and 17
16. The function of the part labeled IV is to enable the fish to
Solution: Part IV (gills) extracts dissolved oxygen from water for respiration. Fins control movement; scales protect.
17. The part labeled V is used for
Solution: Part V (caudal fin/tail) propels and steers the fish. Pectoral/pelvic fins aid balancing; swim bladder controls depth.
18. Which of the following arrangements is a probable food chain?
Solution: Valid food chains start with producers (grass). A follows: producer → herbivore (grasshopper) → carnivores (toad, snake, crow). Others are illogical (e.g., B starts with consumer).
19. One disease which can be transmitted through eating half cooked meat is
Solution: Tapeworm larvae in undercooked meat infect humans. Guinea/hook/thread worms spread via water/soil, not meat.
20. Which of the following characteristics are common to all living things?
I. Response to stimuli
II. Respiration
III. Movement from place to place
IV. Growth
Solution: All living things respond (I), respire (II), and grow (IV). Not all move locationally (e.g., plants—III is false).
21. The part of sugarcane that is usually used for planting is the
Solution: Sugarcane is propagated via stem cuttings (containing nodes for new growth). Seeds (corn) are not typical; leaves/suckers aren’t used.
22. Excess carbohydrate in the human body is stored as
Solution: Glycogen (stored in liver/muscles) is the carbohydrate reserve. Glucose circulates; amino/fatty acids are from proteins/fats.
23. Carbon dioxide in the blood is removed from the body through the
Solution: Lungs expel CO₂ during exhalation. Kidneys remove urea; skin/mouth release minimal gases.
24. The end-product of protein digestion is
Solution: Proteins break down into amino acids for absorption. Glycerol is from fats; glycogen is a carb; peptides are intermediates.
25. The liquid component of the blood is known as
Solution: Plasma (90% water) carries cells/nutrients. Hemoglobin is in RBCs; platelets are cell fragments; cytoplasm is cellular.
26. Digested food substances are absorbed into the blood stream in the
Solution: Ileum (small intestine) has villi for nutrient absorption. Stomach digests; liver processes; kidneys filter blood.
27. The part of the human ear which collect and direct sound waves is the
Solution: Ear canal channels sound to the eardrum. Lobe is external; eardrum vibrates; semicircular canals manage balance.
28. The process by which waste substances are removed from the body is called
Solution: Excretion eliminates metabolic wastes (e.g., urea). Egestion removes undigested food; perspiration is sweat; respiration is gas exchange.
29. The embryo of a mammal develops from
Solution: Mammals are viviparous—internal fertilization and development. External fertilization occurs in fish/amphibians; self-fertilization is rare.
30. Which of the following gases is given out during photosynthesis?
Solution: Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a byproduct. CO₂ is absorbed; carbon monoxide/nitrogen are not involved.
31. The component of the soil which is made up of the finest particles is
Solution: Clay has the smallest particles (<0.002 mm), enabling high water retention. Sand is coarse; loam is a mixture; humus is organic.
32. The soil type which is able to retain the highest amount of water is
Solution: Clay’s fine particles and narrow pores maximize water retention. Sand/gravel drain quickly; loam is moderate.
33. The formation of humus is aided by
Solution: Earthworms decompose organic matter into humus. Insects/rats contribute less directly; wind erodes soil.
34. The major cause of pollution at a stone quarry is
Solution: Quarrying generates airborne dust from rock crushing. Waste/smoke/acid are minor compared to particulate pollution.
35. Ringworm is a skin disease, which is caused by
Solution: Ringworm is a fungal infection (e.g., Trichophyton). Bacteria cause boils; insects/worms don’t cause ringworm.
36. Which of the following habits will help in the control of diseases contracted through air?
I. Not throwing human waste into rivers
II. Washing of hands after visiting the toilet
III. Not spitting about in public places
IV. Keeping foods always covered
Solution: Airborne diseases (e.g., TB) are controlled by reducing spitting (III) and covering food (IV). I prevents waterborne diseases; II targets fecal-oral transmission.
37. Soup which is not well-heated gets spoilt when kept for sometime because the
Solution: Inadequate heating allows bacteria to survive and multiply, spoiling soup. Salt content (A), evaporation (B), and condensation (D) are irrelevant.
38. The measure of the amount of water vapour in the air is known as
Solution: Humidity quantifies air’s water vapor. Clouds are vapor masses; dew is condensed vapor; temperature is heat intensity.
39. Which of the following heavenly bodies is a star?
Solution: The Sun is a star (fusion-powered). Earth is a planet; Moon is a satellite; Milky Way is a galaxy.
40. The planet in our solar system which has the largest orbit is
Solution: Pluto (dwarf planet) has the largest orbit (farthest from the Sun). Jupiter is largest but closer; Mars/Venus are inner planets.
1. QUESTION 1
1. (a) Classify each of the following substances as colloids, suspension or solution:
Smoke, breast milk, powdered milk in water, sea water, mist, steel.
(b) (i) Define valency
(ii) State the valencies of the following elements and radicals:
(a) Iron
(B) Zinc
(y) Hydroxyl
(λ) Carbonate
(c) Give one difference between plants and animals in terms of:
(i) feeding
(ii) excretion
(iii) sensitivity
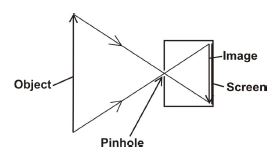
(d) (i) Draw and label a diagram to show how an image is formed in a pinhole camera.
(ii) State the characteristics of the image formed.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1. (a)
- Colloids: Smoke, breast milk, mist
- Suspension: Powdered milk in water
- Solution: Sea water, steel
(b) (i) Valency: The combining power of an atom/ion/radical (determined by the absolute value of the charge).
(ii)
- Iron: 2 or 3
- Zinc: 2
- Hydroxyl: 1
- Carbonate: 2
(c)
Feeding
Plants: Prepare their own food
Animals: Depend on plants/animals for food
Excretion
Plants: Store excretory materials
Animals: Remove excretory materials from body
Sensitivity
Plants: Most do not show sensitivity
Animals: Exhibit high levels of sensitivity
(d) (i)
(ii) Characteristics:
- Real (formed on screen)
- Inverted (upside-down)
- Diminished (smaller than object)
2. QUESTION 2
2. (a) State three differences between molecules in a solid state and liquid state.
(b) (i) What is a solution?
(ii) Difference between solutions and mixtures in terms of particle sizes.
(c) Name the elements which make up the following compounds:
(i) water
(ii) common salt
(iii) ammonia
(d) Copy and complete the table below:
(e) (i) What is a man-made satellite?
(ii) Give two examples of natural satellites.
(iii) Mention two applications of man-made satellites.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2. (a)
Solid State
Molecules closely packed Molecules vibrate in fixed positions Low molecular energy Strong intermolecular forces Molecules widely spaced Molecules move freely High molecular energy Weak intermolecular forces
(b) (i) Solution: A liquid with one/more substances uniformly dissolved in it.
(ii) Difference:
- Solutions: Particles much smaller and evenly distributed.
- Mixtures: Particles larger and unevenly distributed.
(c)
- Water: Hydrogen and oxygen
- Common salt: Sodium and chlorine
- Ammonia: Nitrogen and hydrogen
(d)
(e) (i) Man-made satellite: Artificial body placed in orbit by humans.
(ii) Natural satellites: Moon (orbiting Earth), Earth (orbiting Sun).
(iii) Applications:
- Weather forecasting
- Telecommunication
- TV signal transmission
- Space photography
- Internet networking
- GPS navigation
---
3. QUESTION 3
3. (a) Name the four main parts of a flower.
(b) Give two external features of plants pollinated by wind.
(c) Construct a food chain using any four of the organisms listed below:
Goat, lizard, bird, snake, earthworm, grasscutter, grass, ant, cassava
(d) (i) The energy input of a machine is 7.5 J and the output energy is 5.0 J. Calculate the efficiency.
(ii) Explain why the efficiency of a machine is always less than 1.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3. (a) Four main parts:
- Petal (corolla)
- Sepal (calyx)
- Pistil (style, stigma, ovary)
- Stamen (anther, filament)
(b) Features of wind-pollinated plants (any two):
- Dull-colored petals
- No/low nectar
- No/low scent
- Plentiful light pollen
- Sticky/hairy stigma
(c) Food chains (examples):
- Grass → Earthworm → Bird → Snake
- Cassava → Ant → Lizard → Snake
- Grass → Grasscutter → Snake → Bird
- Cassava → Ant → Bird → Snake
(d) (i) Efficiency:
\[
\text{Efficiency} = \left( \frac{\text{Output}}{\text{Input}} \right) \times 100\% = \left( \frac{5.0 \, \text{J}}{7.5 \, \text{J}} \right) \times 100\% = 66.67\%
\]
(ii) Energy loss occurs due to friction and heat dissipation.
---
4. QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) What is an embryo?
(ii) Where does an embryo develop in the female mammal?
(iii) Describe briefly how a developing embryo breathes in oxygen.
(b) Name three plant nutrients.
(c) (i) What is an electrical insulator?
(ii) Explain how a comb rubbed vigorously on dry hair attracts small pieces of paper.
(d) (i) List the chemical substances used to prepare ammonia gas in the laboratory.
(ii) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) Embryo: Organism post-fertilization (before fetal stage).
(ii) Develops in the uterus/womb.
(iii) Oxygen diffuses from the mother’s blood to the embryo via the placenta.
(b) Plant nutrients (any three):
- Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, Sulphur, Zinc
(c) (i) Electrical insulator: Material that does not allow electric current to pass.
(ii) Rubbing charges the comb. When brought near paper, opposite charges are induced on the paper, causing attraction.
(d) (i) Chemicals: Ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl), Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂).
(ii) Equation:
\[
2\text{NH}_4\text{Cl} + \text{Ca(OH)}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{NH}_3 + \text{CaCl}_2 + 2\text{H}_2\text{O}
\]